What Is a Sodium Ion Cell and How Does It Work
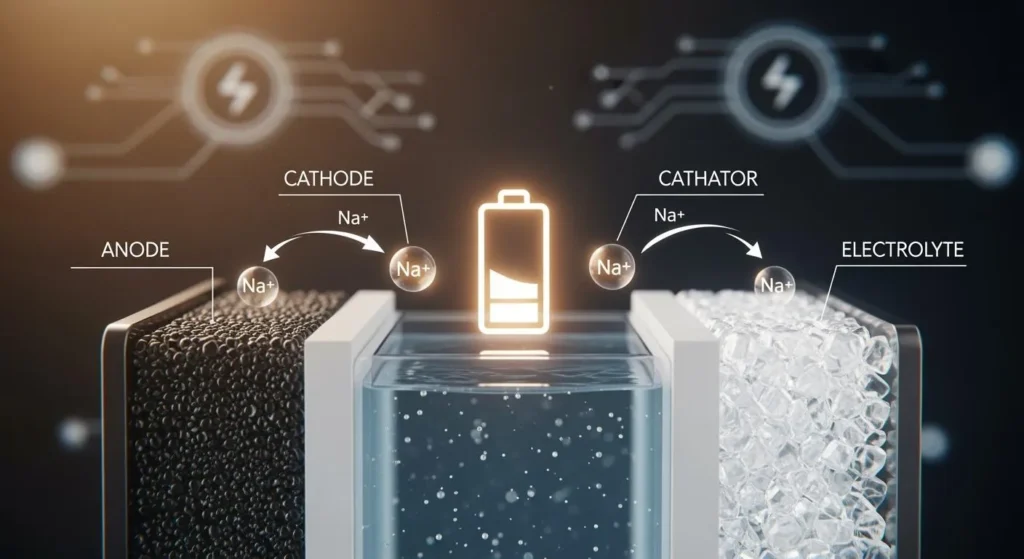
Table of Contents
A sodium ion cell stores and releases electrical energy by moving sodium ions between two electrodes. This process happens inside a closed system where the sodium ion travels through a liquid or solid medium. The sodium ion cell provides reliable power for various devices and systems. It operates efficiently, using sodium ions to transfer charge during both charging and discharging cycles. Companies and industries use sodium ion cells for their safety and stable performance.
- The sodium-ion battery market reached $321.75 million in 2023.
- Experts project the market will grow to $2.24 billion by 2026, with a CAGR of over 15% through 2034.
Key Takeaways
- Sodium ion cells store energy by moving sodium ions between two electrodes, providing reliable power for various applications.
- These batteries are safer and more sustainable than lithium-ion batteries due to the abundance of sodium and lower environmental impact.
- Sodium ion batteries can charge faster than lithium-ion batteries, making them ideal for quick energy storage solutions.
- The unique design of sodium ion cells allows them to perform well in extreme temperatures, ensuring reliability in cold climates.
- Sodium ion technology is rapidly growing, with projections showing significant market expansion and increased adoption in electric vehicles and renewable energy.
Sodium Ion Cell Components
A sodium cell contains several key parts that work together to store and release energy. Each component has a specific role in the cell’s operation. Understanding these parts helps explain how the sodium cell delivers reliable power for many applications.
Cathode and Anode
The cathode and anode are the two main electrodes in a sodium cell. The anode, often made from hard carbon or titanium-based materials, stores sodium ions during charging. These materials provide a stable structure, which helps the cell last longer and operate safely. The cathode uses layered transition metal oxides or polyanionic compounds. These materials allow sodium ions to move in and out easily, supporting high capacity and good conductivity.
| Material Type | Role | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Hard Carbon / Titanium-Based | Anode | Stable structure, long cycle life, safe operation |
| Layered Oxides / Polyanions | Cathode | High capacity, fast sodium ion movement, strong safety performance |
🟦 Tip: The anode and cathode act as hosts for sodium ions, allowing the cell to charge and discharge efficiently.
Electrolyte and Separator
The electrolyte in a sodium cell is a sodium salt dissolved in a liquid or gel. It acts as a pathway for sodium ions to travel between the cathode and anode. The separator is a thin, porous layer that sits between the electrodes. It prevents direct contact while letting sodium ions pass through. The quality of the separator affects the cell’s safety, capacity, and cycle life. Improvements in separator design can boost the overall performance of sodium cells.
- The electrolyte enables smooth movement of sodium ions.
- The separator keeps the electrodes apart and supports safe operation.
Current Collectors
Current collectors are thin metal sheets that carry electrical current in and out of the sodium cell. Copper and aluminum are common choices. Copper offers lower electrical resistance and higher thermal conductivity, making it ideal for high-power uses. Aluminum is lighter but has higher resistance, which can affect performance in demanding applications.
| Current Collector | Electrical Resistivity | Thermal Conductivity | Impact on Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copper (Cu) | Low | High | Best for high-power applications |
| Aluminum (Al) | Higher | Lower | Suitable for standard applications |
🔋 Note: The right choice of current collector helps the sodium cell deliver power efficiently and safely.
For more details about battery components, industry professionals often refer to resources like Battery University or ScienceDirect.
How Sodium Ion Cells Work
Understanding the working principle of a sodium ion cell requires a close look at how sodium ions move between the electrodes during charging and discharging. This movement forms the foundation of energy storage and release in sodium ion technology.
Charging and Discharging
The charging and discharging process in a sodium ion cell follows a clear sequence. Each step involves the controlled movement of sodium ions, which enables the cell to store and deliver electrical energy efficiently.
Charging Process 🔌
- The charger applies an external voltage to the sodium ion cell.
- Sodium ions leave the cathode and travel through the electrolyte.
- These sodium ions embed themselves into the anode’s structure, usually made of hard carbon.
- Electrons flow through the external circuit to balance the charge.
- The cell stores energy as sodium ions accumulate in the anode.
Discharging Process ⚡
- The device draws power from the sodium ion cell.
- Sodium ions move from the anode back to the cathode through the electrolyte.
- Electrons flow through the external circuit, powering the connected device.
- The cell releases stored energy as sodium ions return to the cathode.
Note: The movement of sodium ions between the electrodes is essential for both storing and releasing energy.
The voltage range during these processes determines the cell’s performance and safety. The table below summarizes typical voltage values for sodium ion cells:
| Voltage Type | Voltage Range |
|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | ~3.2V |
| Full Charge Voltage | ~3.6–3.7V |
| Cutoff Voltage | ~2.5–2.8V |
Sodium ion cells can charge faster than lithium-ion cells because they generate less heat. This advantage allows for higher charging speeds, often reaching up to 3C, compared to 2C for lithium batteries. The table below compares the charging and discharging process in sodium ion and lithium-ion cells:
| Process | Sodium-Ion Cells | Lithium-Ion Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Charging | Sodium ions move from the cathode to the anode, depositing in the carbon structure. | Lithium ions move from the cathode to the anode. |
| Discharging | Sodium ions move back to the cathode, releasing energy. | Lithium ions move back to the cathode, releasing energy. |
For a detailed explanation of battery operation, industry professionals often consult Battery University or ScienceDirect.
Role of Sodium Ions
Sodium ions play a central role in the working principle of sodium ion cells. Their movement between the electrodes enables the cell to function as an energy storage device.
- Sodium ions (Na⁺) shuttle between the cathode and anode during charging and discharging.
- During charging, sodium ions leave the cathode, pass through the electrolyte, and embed into the anode.
- During discharge, sodium ions return to the cathode, releasing energy that powers devices.
- The flow of sodium ions creates an electric current, which is essential for the operation of the cell.
- Sodium ions are responsible for the reversible energy storage and release in sodium ion batteries.
- The working principle relies on the ability of sodium ions to move efficiently and repeatedly without degrading the cell’s materials.
- The design of the electrodes and electrolyte ensures that sodium ions can travel with minimal resistance, supporting long cycle life and stable performance.
💡 Tip: The efficiency and reliability of sodium ion cells depend on the smooth movement of sodium ions during every cycle.
Sodium ion technology continues to advance, offering safe, fast-charging, and environmentally friendly solutions for energy storage. The unique working principle and the role of sodium ions make these cells suitable for a wide range of industrial and commercial applications.
For further reading on sodium ion cell operation, visit Nature Energy or ScienceDirect.
Sodium Ion Battery vs. Lithium-Ion

Key Differences
Sodium ion battery and lithium-ion batteries serve similar roles in energy storage, but they differ in several important ways. The most notable differences include energy density, cost, abundance, safety, and environmental impact.
| Battery Type | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Cycle Life (Cycles) | Raw Material Abundance | Safety Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium-ion | 150–250 | ~1,000–5,000 | Scarce | Medium |
| Sodium ion battery | 100–160 | ~2,000–4,000 | Highly abundant | High |
- Sodium ion battery uses sodium, which is about 1,000 times more abundant than lithium. This abundance leads to lower raw material costs and a more sustainable supply chain.
- Lithium-ion batteries rely on critical minerals such as cobalt and nickel, which face supply constraints and environmental concerns.
- Sodium-ion batteries generally offer better thermal stability and lower fire risk.
- The energy density of sodium ion battery is about 30% lower than lithium-ion batteries, but sodium-ion batteries maintain their charge better in cold conditions.
- Both sodium ion battery and lithium-ion batteries have similar costs per kWh, but sodium-ion batteries may offer lower operational costs over time.
🔍 For a detailed comparison, visit ScienceDirect’s sodium-ion vs. lithium-ion battery overview.
Advantages of Sodium Ion Batteries
Sodium-ion batteries provide several advantages for commercial and industrial applications:
- They avoid reliance on rare metals, reducing supply chain risks.
- Sodium ion battery production has a smaller environmental footprint than lithium-ion batteries.
- Sodium-ion batteries do not require cobalt or nickel, minimizing social and ecological costs.
- These batteries offer high safety, with a lower risk of thermal runaway and non-flammable chemistry.
- Sodium-ion batteries maintain stable performance in extreme temperatures, supporting reliable operation in cold climates.
- The cycle life of sodium ion battery can reach up to 4,000 cycles, with some lab tests exceeding 5,000 cycles.
- Sodium-ion batteries are suitable for grid-scale energy storage, telecom, and mobility solutions.
⚡ Sodium-ion batteries help reduce operational costs, with up to 90% less auxiliary power use due to passive cooling.
VEKEN Sodium Battery Features
VEKEN Sodium Battery stands out in the sodium ion battery market with unique features:
| Feature | VEKEN Sodium Battery | Industry Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Safety | No lead or heavy metals | May contain harmful materials |
| Cold Weather Performance | Reliable at −40 °C | May degrade in cold |
| Customization | Highly customizable | Limited options |
| Lamination Technology | Enhanced heat control | Standard construction |
| Warranty and Support | Long-term, fast response | Varies |
| Certifications | ISO 9001, ISO 14001, UN38.3, MSDS, CE, RoHS, CB | Varies |
- VEKEN Sodium Battery operates from −40 °C to 80 °C, supporting diverse applications such as energy storage systems, commercial power, and mobility solutions.
- The battery maintains stable output in cold and hot environments, ensuring year-round reliability.
- VEKEN Sodium Battery uses advanced lamination technology for improved heat control and safety.
- The battery meets international certifications, supporting global deployment and safe transportation.
🏆 VEKEN Sodium Battery delivers high safety, long cycle life, and robust performance for demanding energy storage needs.
For more information, visit VEKEN Sodium Battery official site.
Applications and Future of Sodium Ion
VEKEN Sodium Battery Applications
Sodium ion batteries have become essential in many industries due to their safety, cost-effectiveness, and reliable performance. Companies use these batteries in a variety of real-world applications:
- Household Energy Storage: Homeowners use sodium ion batteries in residential energy storage systems. These systems store electricity from solar panels or the grid, providing backup power during outages. The world’s first sodium ion battery household energy storage system launched in 2022, marking a major milestone for the industry.
- Large-Scale Energy Storage: Utilities and grid operators deploy sodium ion batteries for large-scale energy storage. These batteries support renewable energy integration and stabilize power supply. They offer long service life, often exceeding 10,000 cycles and lasting up to 20 years.
- Backup Power Systems: Telecom companies rely on sodium ion batteries for backup power in base stations and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS). These batteries ensure continuous operation during power interruptions.
- Electric Mobility: Sodium ion batteries power electric bicycles, motorcycles, urban delivery vehicles, and public transportation. They perform well in cold climates, making them ideal for commercial vehicles and logistics fleets in regions like Northern China and Eastern Europe.
- Data and Communication Centers: IT and telecom sectors use sodium ion batteries in equipment racks to maintain stable operations.
| Use Case Description | Location Relevance |
|---|---|
| Commercial vehicles operating in cold regions | Northern China, Central Asia, Eastern Europe |
| Logistics fleets with overnight parking | Northern China, Central Asia, Eastern Europe |
| Vehicles needing stable auxiliary power in winter | Northern China, Central Asia, Eastern Europe |
| Fleet operators seeking alternatives to lead-acid batteries | Northern China, Central Asia, Eastern Europe |
🚚 Tip: VEKEN Sodium Battery supports demanding environments, offering high safety and stable output even at −40 °C. For more on real-world deployments, see Sodium-Ion Battery News.
Future Outlook
Sodium-ion technology continues to evolve, driven by innovation and growing market demand. Recent advancements in cathode materials, such as layered oxides and Prussian blue analogues, have improved battery performance and lifespan. Hard carbon anodes and new electrolyte formulations further enhance energy density and safety.
The sodium ion battery market is set for rapid growth:
| Year | Market Size (USD) | CAGR (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2026 | 566.65 billion | 23.32 |
| 2035 | 3,736.98 billion | |
| 2040 | 10,656.96 billion |
Manufacturers and research teams focus on expanding sodium-ion technology into electric vehicles and renewable energy storage. Projects in Germany and investments by companies like Northvolt and Altris highlight the global commitment to this field. Governments support the industry with funding, tax credits, and research hubs to boost manufacturing and innovation.
Recent breakthroughs, such as sodium-ion pouch cells that operate at extremely low temperatures, show the potential for even broader adoption. As sodium ion batteries address raw material limitations and price volatility in lithium-ion batteries, they offer a sustainable and cost-effective solution for future energy needs.
🌱 Note: Sodium-ion technology will play a key role in the transition to clean energy, supporting grid stability, electric mobility, and sustainable development. For case studies and updates, visit ScienceDirect Sodium-Ion Battery Applications.
Sodium ion cells deliver reliable energy storage by moving sodium ions between electrodes. They support grid stability, renewable integration, and long cycle life. The table below highlights their main features:
| Feature | Sodium-Ion Batteries |
|---|---|
| Energy Density | 90–160 Wh/kg (suitable for residential and grid storage) |
| Cycle Life | 2,000–4,000 cycles (improving with R&D) |
| Efficiency | Comparable round-trip efficiency (85–90%) to lithium-ion |
| Grid Stability | Can store excess renewable energy for peak demand |
| Renewable Integration | Ideal for solar farms and wind projects |
| Scalability | Adapt existing lithium-ion production lines with minimal changes |
VEKEN Sodium Battery stands out for its safety, temperature tolerance, and customizable solutions. Key advantages include:
- Sodium’s abundance ensures sustainable supply.
- Low maintenance and long service life reduce operational costs.
- Systems support renewable energy storage and grid reliability.
“Deploying the world’s largest sodium-ion energy storage system with one of the nation’s top independent power producers proves that sodium is ready for today and will dominate the future,” said Peak Energy CEO and co-founder Landon Mossburg.
Sodium ion technology will shape the future of energy storage, supporting clean energy transitions and powering diverse industries worldwide.
FAQ
What are the main benefits of sodium-ion batteries for commercial energy storage?
Sodium-ion batteries offer high safety, long cycle life, and stable performance in extreme temperatures. Businesses use them for grid storage, telecom backup, and renewable energy integration. These batteries reduce operational costs and support sustainable energy solutions.
Can VEKEN sodium batteries operate in cold climates?
VEKEN sodium batteries maintain reliable output at temperatures as low as −40 °C. Companies in Northern China and Eastern Europe deploy these batteries for logistics fleets, telecom stations, and residential energy storage systems in harsh winter conditions.
How do sodium-ion batteries compare to lead-acid batteries in industrial applications?
Sodium-ion batteries deliver over five times longer cycle life than lead-acid batteries. They tolerate deep discharge and require less maintenance. Industrial users benefit from reduced replacement costs and improved safety during transportation and storage.
Are VEKEN sodium batteries customizable for specific business needs?
VEKEN offers fully customizable sodium battery solutions. Clients select operating temperature range, cell model, configuration, voltage, and capacity. This flexibility ensures optimal performance for motorcycles, agricultural machinery, and large-scale energy storage projects.
What certifications do VEKEN sodium batteries hold for global deployment?
VEKEN sodium batteries meet international standards, including ISO 9001, ISO 14001, UN38.3, MSDS, CE, RoHS, and CB. These certifications support safe transportation, installation, and operation in commercial and industrial environments worldwide.
Quick Link
Contact
Address
Floor 18, Yuehu Jinhui Tower, 225 Liuting Street Haishu District,Ningbo,China 315010
Copyright © 2025 , All rights reserved. Powered by ningbo v.k. industry & trading Co., Ltd.