Unveiling how sodium-ion batteries are made and the materials behind their performance
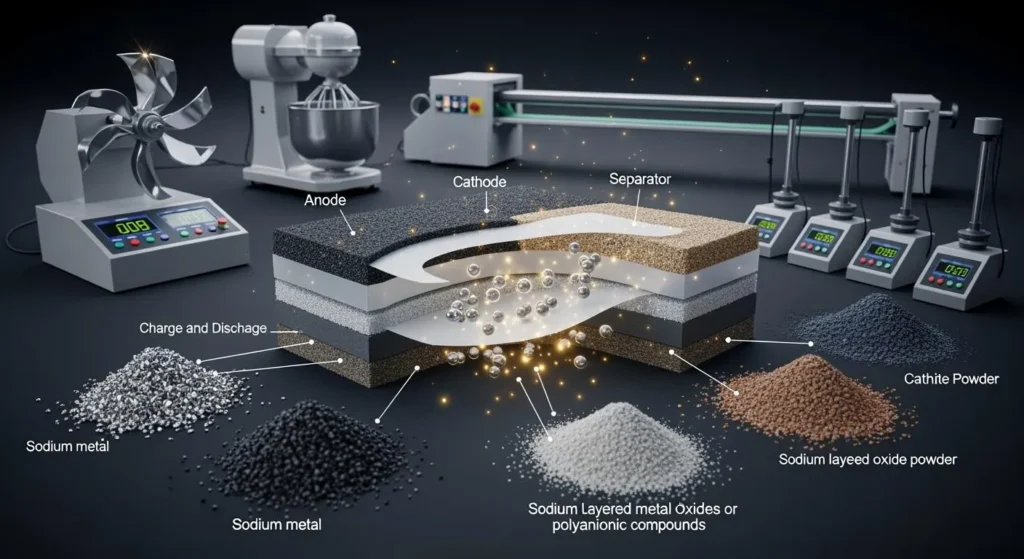
Table of Contents
You see sodium-ion batteries made with care and new technology. Makers pick materials that help the battery work well and last long. Welsh coal-derived composite carbon is a key part. It helps the sodium-ion battery work better. VEKEN is a top company using new ideas to make sodium-ion batteries. Sodium is very important in the battery’s chemistry. This lets you use safe and earth-friendly energy.
Key Takeaways
- Sodium-ion batteries use sodium, not lithium. This makes them safer and better for the environment.
- VEKEN uses good materials like hard carbon and layered oxides. These help the battery work better and last longer.
- The process to make them needs careful picking of materials. They also clean the materials and check quality to make sure they work well.
- Sodium-ion batteries charge quickly and do not cost a lot. This makes them a smart choice for storing energy.
- VEKEN helps customers and gives special solutions for different energy storage needs.
Sodium-ion battery technology at VEKEN
What makes sodium-ion batteries unique
Sodium-ion batteries are a new way to store energy. They use sodium, not lithium. Sodium is easy to find and safe. These batteries can charge faster than lithium-ion batteries. Hard carbon helps them charge quickly. They work well when you need a lot of power. They stay steady while working. You can trust them in many places.
Some things make sodium-ion batteries special:
- They charge faster than many other batteries.
- The materials are easy to get.
- They work well even when it is hard.
- Their energy density is like other good batteries.
VEKEN’s approach to battery innovation
VEKEN has made things for a long time. The company started in 1905. It is known for being strong in the business. VEKEN has an AAA credit rating. This means you can trust their products. VEKEN is a leader in making sodium-ion batteries. They use new materials and smart ways to build them.
You can look at how VEKEN’s batteries compare to others:
| Feature | VEKEN Sodium-Ion Batteries | Competitors’ Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density (Wh/kg) | 90-150 | Higher in some cases |
| Cycle Life | Long | Varies |
| Safety | High | Varies |
VEKEN answers your questions fast. Their team helps you pick the best solar battery. Many people say VEKEN’s batteries work well with their systems. When you pick VEKEN, you get batteries made with care and safe materials.
Manufacturing process of sodium-ion batteries
You can watch how sodium-ion batteries are made step by step. Each part uses new technology and careful checks. VEKEN uses a trusted way to make sure the batteries work well for your business.
Material selection and preparation
First, you pick the best materials. VEKEN gets high-purity sodium and hard carbon for the anode. The team chooses layered oxide or polyanionic compounds for the cathode. These choices change how much energy the battery can hold and give out. You also need a strong electrolyte and a separator to keep the anode and cathode apart.
Tip: Good materials help the battery work better and stay safe.
Here is an easy list of the steps:
- Sourcing: You get sodium, hard carbon, cathode compounds, electrolyte, and separator from trusted places.
- Purification: You clean each material to take out anything bad.
- Mixing: You mix the main parts with binders and additives to help them work better.
- Coating: You spread the mix on thin metal foils to make the anode and cathode layers.
Image: Schematic of sodium-ion battery materials and structure 🧪
You can find more about battery materials at ScienceDirect.
Electrode and cell assembly
Next, you put the battery together. The coated foils turn into electrodes. You cut them into the right shapes. You stack or roll the anode and cathode with a separator in the middle. This makes the main part of the cell.
Here are the steps in order:
- Stacking: You put the anode, separator, and cathode in layers.
- Electrolyte filling: You add the electrolyte so sodium ions can move.
- Sealing: You close the cell in a case to stop leaks and dirt.
- Formation: You charge and use the cell to get the materials ready and steady.
| Step | Purpose | Impact on Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Stacking | Puts electrodes and separator together | Keeps it safe |
| Electrolyte fill | Lets ions move | Makes it work better |
| Sealing | Protects the inside | Helps it last longer |
| Formation | Gets battery chemistry started | Makes output steady |
Quality assurance and packaging
You check each battery to make sure it is good. VEKEN uses machines to test voltage, capacity, and safety. You look at every cell for problems. Only batteries that pass all tests get packed.
Note: VEKEN’s quality checks help lower risk and make batteries more reliable.
You wrap the batteries in safe materials. You put labels with codes on each one. This lets you track every batch and keeps delivery safe.
Key points in VEKEN’s quality process:
- Machines test every cell
- People look for problems
- Labels and packaging help track each battery
- Follows world safety rules
You can count on VEKEN’s sodium-ion batteries to work the same every time. The steps from picking materials to packing make sure you get a battery you can trust.
Key materials in sodium-ion batteries
You need to know about the main materials in sodium-ion batteries. Each material has a special job. It helps the battery store and give out energy. VEKEN picks and designs these materials for good performance, safety, and low cost.
Hard carbon anodes
Hard carbon is the top choice for the anode in sodium-ion batteries. Its special structure lets sodium ions move fast and store well. Hard carbon comes from things like lignin, which is found in plants. The closed-pore structure helps the battery hold more energy and charge quickly.
- High reversible specific capacity (up to 358 mAh g−1) means more energy can be stored in each gram.
- The porous structure lets sodium ions go in and out easily, so charging is faster.
- Lignin-based hard carbon has about 60% carbon and lots of oxygen groups. These help make the right pores for sodium storage.
Tip: Hard carbon’s low-crystalline form and tiny holes let sodium gather and move with less energy. This makes batteries charge faster and last longer.
New hard carbon technology has made sodium-ion batteries work even better. You can see how these changes help:
| Advancement | Description |
|---|---|
| Charging Speed | Hard-carbon anodes let batteries charge faster than lithium-ion batteries. |
| Diluted Electrode | Mixing hard carbon with aluminum oxide stops ion traffic jams. |
| Ion Mobility | Sodium ions move through hard carbon faster than lithium ions. |
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Pre-sodiation | Adds extra sodium to make up for losses, so energy density and battery life get better. |
| Scalability | Makes pre-sodiation methods work well and cost less for big factories. |
You can read more about hard carbon anodes in sodium-ion batteries at ScienceDirect.
Image: Hard carbon structure for sodium storage ⚡
Cathode materials and performance
The cathode decides how much energy your battery gives and how long it lasts. VEKEN uses special cathode materials, like layered oxides and polyanionic compounds, for high capacity and strong stability.
O3-type nickel-manganese-based layered cathodes are good for making high-energy sodium-ion batteries for growing energy storage needs. But, tricky phase changes and slow Na+ movement have made them hard to use. This work uses a medium-entropy plan for O3-type NaNi0.5Mn0.5O2 cathode to change the covalency of Ni/Mn-O bonds. This makes the structure stronger and helps Na+ move better. The new O3-Na0.92Ni0.47Nb0.03Mn0.30Ti0.20O2 (NNNMTO) works well at different speeds and lasts a long time, so it is good for real use.
You can compare how different cathode materials perform in this table:
| Cathode Material | Discharge Capacity (mAh g-1) | C-rate Performance (mAh g-1) at Various Rates | Cycling Stability |
|---|---|---|---|
| P2-Naₓ(FeᵧMn₁⁻ʸ)O₂ | 164.2 | 147.2 at 200 mA g-1, 115.3 at 500 mA g-1, 99.6 at 1000 mA g-1, 82.3 at 2000 mA g-1 | Acceptable |
| O3-Na(FeMn₁₋ᵧ)O₂ | N/A | N/A | N/A |
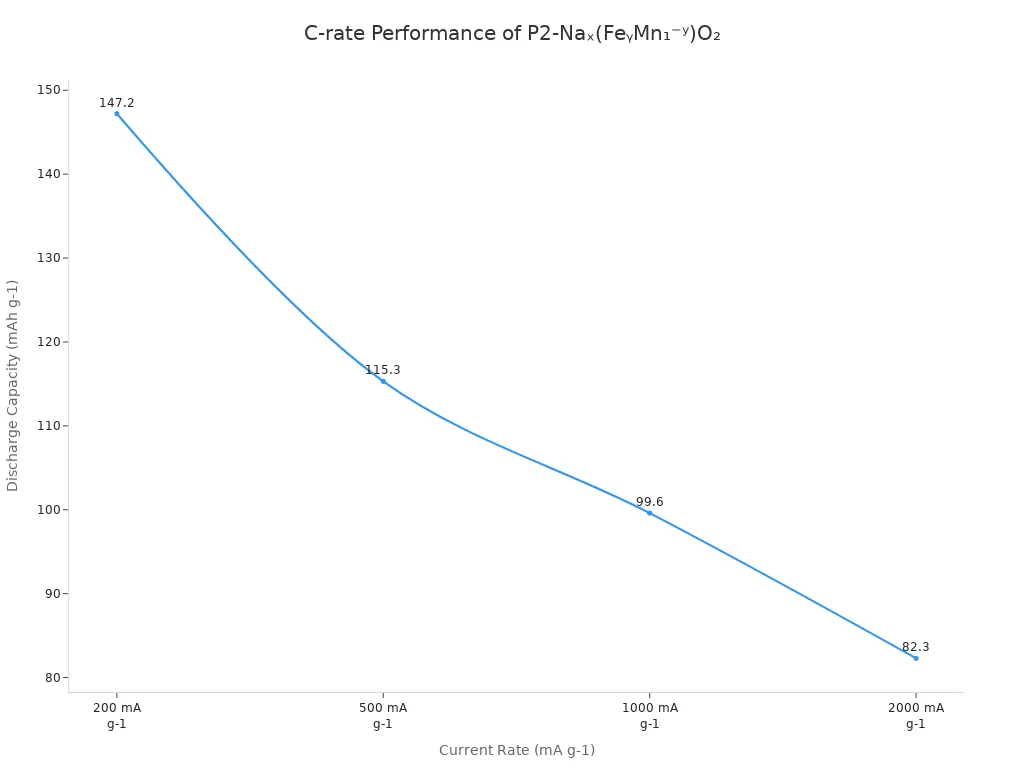
You get steady power and long life when you pick the right cathode materials. These choices help your battery work well, even when charging and using power quickly.
Electrolytes and separators
The electrolyte and separator work together to keep your battery safe and working well. The electrolyte lets sodium ions move between the anode and cathode when charging and using the battery. A stable electrolyte stops leaks and overheating, so your battery stays safe.
The separator sits between the anode and cathode. It keeps them from touching and causing a short circuit. It also lets sodium ions pass through. This design keeps your battery safe and helps it run smoothly.
Note: Electrolytes in sodium-ion batteries are very important because they help sodium ions move between the electrodes, which is needed for the battery to work. The stability of the electrolyte is key for stopping problems like overheating and leaks. Separators help keep the battery safe by stopping short circuits and making sure the electrolyte stays in place, so the battery works well and is safe.
You can see how each material helps the battery work:
- Hard carbon anodes store sodium well and help fast charging.
- Special cathode materials give high energy and long life.
- Stable electrolytes and strong separators keep the battery safe and steady.
When you pick sodium-ion batteries from VEKEN, you get a product made with care. These materials give you energy storage that is efficient, low-cost, and reliable for your business.
Innovations and challenges in sodium-ion battery manufacturing
Advancements in materials
Sodium-ion battery technology is getting better very quickly. In the last five years, scientists made the cathode stronger by changing NaNi1/3Fe1/3Mn1/3O2. This new cathode can store more energy and is more stable. Now, it can reach 596 Wh kg-1 based on the cathode’s weight. That is 15% better than older types. This means batteries last longer and work well in hot or cold places. These changes also make batteries safer and cost less to make. Because of this, more companies use sodium-ion batteries for big energy storage. They help keep the power grid steady and handle busy times. The batteries have a modular design, so you can pick what fits your needs. Rules and the need to cut pollution also help more people use these batteries.
For more about new battery materials, check Nature Energy.
Overcoming production challenges
Making sodium-ion batteries is not always easy. VEKEN uses special plans to fix these problems:
| Strategy Description | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Long-term partnerships with clients | Gives support and flexible supply chains |
| Custom battery design | Makes the right size and shape for your project |
| Post-purchase assistance | Offers training, guides, and answers to your questions |
| Custom solutions | Saves money and gives you more value |
| AI-powered monitoring and safety tools | Lowers costs for fixing and setting up batteries |
VEKEN helps you from the start to the end, even after you buy.
Future trends at VEKEN
VEKEN will keep leading new ideas for sodium-ion batteries. They focus on strong power, long life, and safety in all kinds of weather. You can ask for batteries made just for your project. VEKEN gives you help and training when you need it. They use local materials for the anode, cathode, and electrolyte. This keeps prices steady and makes sure you get your batteries on time.
🛠️ VEKEN’s promise to use good materials and give great support helps you do well as energy storage changes.
You now know how sodium-ion batteries are made. People pick the right materials for each battery. They put the parts together with care. Every battery goes through many safety checks. Hard carbon and special cathodes help the battery work well and stay safe. VEKEN uses new ideas and checks quality at every step. As people need more ways to store energy, sodium-ion batteries will become more important. VEKEN will keep making better batteries and lead the way in battery technology.
FAQ
❓ What makes sodium-ion batteries a good choice for grid energy storage?
Sodium-ion batteries work well for grid energy storage. They last a long time and use cheaper materials. These batteries help keep power steady in big systems. They make sure supply and demand match. You can learn more at U.S. Department of Energy.
⚡ How does electrolyte formulation affect battery safety?
The right electrolyte mix keeps your battery safe. It stops the battery from getting too hot or leaking. This helps the battery work well every time. For more details, visit ScienceDirect.
🏭 Can you recycle sodium-ion batteries after use?
You can recycle sodium-ion batteries when they are used up. Recycling lets us get back important materials and cuts down on waste. Many companies now recycle batteries from big storage systems. Read more at International Energy Agency.
🔋 What is the main difference between sodium-ion and lithium-ion batteries?
Sodium-ion batteries use sodium, not lithium. Sodium is easier to find and costs less. Both types store energy, but sodium-ion batteries are safer and better for the planet when used in big projects. See Clean Energy Institute.
🛠️ How do you ensure quality in sodium-ion battery manufacturing?
Quality comes from using good testing tools and careful checks. Each battery must pass safety and performance tests before it ships. Labels on the packages help track every battery. For industry standards, refer to UL Standards.
Quick Link
Contact
Phone
0086-574-87208762
info@vekenindustry.com
Address
Floor 18, Yuehu Jinhui Tower, 225 Liuting Street Haishu District,Ningbo,China 315010
Copyright CleanMonk © 2025 All Rights Reserved