Is a Sodium Battery Better Than Lithium for Performance?

Table of Contents
You may be asking yourself, is a sodium battery better than lithium? When comparing the two, sodium-ion batteries now charge faster and last longer, but lithium-ion batteries still offer higher energy density. This is important when considering electric vehicles and energy storage. If you’re wondering, is a sodium battery better than lithium for charging speed, sodium-ion batteries can recharge in just 20 minutes and last up to 10,000 cycles. On the other hand, lithium-ion batteries require more careful handling but deliver more power in a smaller package.
Performance Metric | Sodium-Ion | Lithium-Ion |
|---|---|---|
Energy Density | 100–160 Wh/kg | 150–250 Wh/kg |
Charging Speed | ~20 minutes | Slower |
Cycle Life | Up to 10,000 | 5,000–8,000+ |
Is a sodium battery better than lithium in market share? Currently, sodium-ion batteries hold about 5% of the market.
The market for sodium-ion batteries may grow to 30% by 2030, especially for energy storage.
Regions with abundant sodium resources are investing in sodium-ion technology to boost energy independence.
So, is a sodium battery better than lithium for your needs? Consider what matters most to you—charging speed, energy density, safety, or cost—before making your choice.
Key Takeaways
Sodium-ion batteries charge faster, reaching full charge in about 20 minutes, making them ideal for quick energy needs.
Lithium-ion batteries have higher energy density, meaning they store more energy in a smaller size, perfect for electric vehicles and portable devices.
Sodium-ion batteries are generally cheaper and more eco-friendly, using abundant materials and being easier to recycle.
For safety, sodium-ion batteries have a lower risk of overheating and can be safely discharged to zero volts, making them safer for storage.
Choosing between the two depends on your needs: go for sodium-ion for fast charging and cost savings, or lithium-ion for high performance and energy density.
Is a Sodium Battery Better Than Lithium?
Key Performance Differences
When you ask, is a sodium battery better than lithium?, you need to look at several important features. Sodium-ion batteries charge faster and can last longer in some tests, but lithium-ion batteries still lead in energy density and reliability. You will find that sodium-ion batteries use hard carbon electrodes, which help sodium ions move quickly. This means you can recharge them faster than most lithium-ion batteries. Some studies show sodium-ion batteries can reach a full charge in about 20 minutes. However, other research points out that ion diffusion can slow down charging in certain designs.
Let’s compare the main features side by side:
Feature | Sodium-Ion Batteries | Lithium-Ion Batteries |
|---|---|---|
Energy Density | Lower (about 30% less) | Higher |
Often faster | Slower | |
Cycle Life | 5,000–8,000+ cycles | |
Mass | Heavier | Lighter |
Safety | Less risk of overheating | More risk of overheating |
Cost | More expensive | |
Environmental Impact | More eco-friendly | Less eco-friendly |
Market Readiness | Newer, less common | Proven, widely used |
You may notice that sodium-ion batteries have a lower energy density. This means they store less energy for the same size and weight. Lithium-ion batteries are lighter and can pack more power into a smaller space. This makes them a better choice for electric vehicles and portable devices. On the other hand, sodium-ion batteries stand out for their safety and cost. They have a lower risk of overheating and use materials that are easier to find and better for the planet.
Tip: If you want a battery that charges quickly and costs less, sodium-ion might be the right choice. If you need more power in a small space, lithium-ion is still the leader.
Which Is Best for Your Needs?
Is a sodium battery better than lithium? The answer depends on what you need most. If you care about fast charging and safety, sodium-ion batteries offer strong advantages. They use materials that are easy to find and do not need rare metals like cobalt or nickel. This makes them cheaper and more sustainable. You can also safely discharge sodium-ion batteries to zero volts, which helps with storage and transport.
If you want the highest energy density and proven performance, lithium-ion batteries remain the top pick. They work best in electric vehicles, smartphones, and laptops. Their lighter weight and higher voltage give you more power for longer periods. You will also find more charging stations and replacement options for lithium-ion batteries because they have been around longer.
Here are some things to consider when choosing between the two:
Cost: Sodium-ion batteries are usually cheaper because sodium is common and easy to get.
Safety: Sodium-ion batteries have a lower chance of overheating.
Energy Density: Lithium-ion batteries store more energy in a smaller size.
Environmental Impact: Sodium-ion batteries are more eco-friendly and do not use rare metals.
Availability: Lithium-ion batteries are easier to find and have more support in the market.
Is a sodium battery better than lithium? For large-scale energy storage, like supporting the electrical grid, sodium-ion batteries may soon become the top choice. Experts predict that by 2026, about 70% of sodium-ion batteries will be used for energy storage. For electric vehicles and portable devices, lithium-ion batteries still hold the advantage because of their higher energy density and lighter weight.
Note: Your best choice depends on your priorities. If you want to save money and help the environment, sodium-ion batteries are a smart pick for stationary uses. If you need high performance in a small package, lithium-ion batteries are still the best option.
Energy Density

Lithium-ion Density
You will notice that lithium-ion batteries lead the market in energy density. This means they can store more energy in a smaller and lighter package. You can see the differences in the table below:
Battery Type | Energy Density (Wh/kg) |
|---|---|
LTO (Lithium Titanate) | 50-80 |
Lithium Cobalt Oxide | 150-200 |
Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide | 150-220 |
LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) | 90-160 |
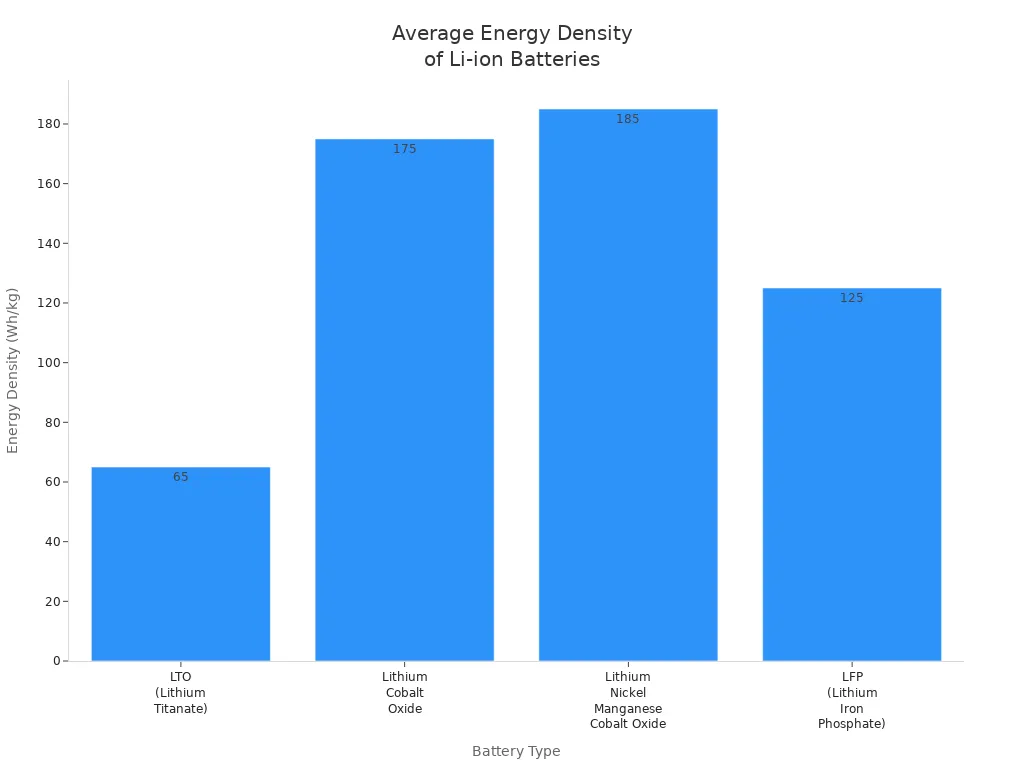
Higher energy density gives you longer battery life. You can use your phone or laptop for more hours without charging. Devices stay slim and light because the batteries do not take up much space or add much weight.
Sodium-ion Density
Sodium-ion batteries have made progress, but they still lag behind lithium-ion batteries in energy density. Most sodium-ion batteries today reach about 150-160 Wh/kg. Some new designs can go a bit higher, but they do not match the top lithium-ion batteries. Because sodium atoms are larger and heavier than lithium atoms, sodium-ion batteries need more space for the same amount of energy.
Sodium-ion batteries: 150-160 Wh/kg
Lithium-ion batteries: 200-300 Wh/kg
You will find that sodium-ion batteries are bigger and heavier if you want the same power as a lithium-ion battery.
Impact on Applications
Energy density affects how you use batteries in real life. If you want a battery for a phone, laptop, or electric car, you need something small and powerful. Lithium-ion batteries work best for these uses because they pack more energy into less space. You get longer range in electric vehicles and lighter devices in your backpack.
Sodium-ion batteries work well for large, stationary uses. You might see them in grid storage or backup power systems. Their lower energy density means they are not the best choice for portable electronics or cars that need to go far on a single charge. Is a sodium battery better than lithium? For high-power and mobile applications, lithium-ion batteries still win because of their higher energy density.
Tip: If you care about size and weight, choose lithium-ion. If you need a safe and cost-effective battery for large storage, sodium-ion is a smart pick.
Charging Speed
Fast Charging: Sodium vs. Lithium
You might wonder how quickly you can charge a sodium-ion battery compared to a lithium-ion battery. Charging speed matters a lot when you want to get back on the road or power up your devices fast. Recent research shows that sodium-ion batteries can reach 80% charge in as little as 6 minutes. Some lithium-ion batteries can charge to 80% in 15 minutes or less, but most take about 30 minutes. Here is a quick comparison:
Battery Type | Charging Time to 80% SOC |
|---|---|
Lithium-ion | 30 min |
Lithium-ion | 15 min or less |
Sodium-ion | 6 min |
Sodium-ion batteries use special hard carbon electrodes. These electrodes have a low-crystalline and porous structure. This design lets sodium ions move quickly and store energy fast. Scientists also use a diluted electrode method, which gives sodium ions easy access to the electrode. Sodium ions can move faster than lithium ions in these materials. The process of filling the pores with sodium takes less energy than with lithium, so you get a faster charge.
Hard carbon electrodes allow fast sodium storage.
Diluted electrode methods remove ion transport limits.
Sodium ions move faster in hard carbon than lithium ions in graphite.
The pore-filling step uses less energy for sodium, speeding up charging.
Real-World Use Cases
You will see the benefits of fast charging in many real-life situations. If you drive an electric car, a sodium-ion battery could let you recharge during a short break. For buses or delivery vehicles, quick charging means less downtime and more time on the road. In home energy storage, you can store solar power quickly when the sun shines. Is a sodium battery better than lithium? For charging speed, sodium-ion batteries often give you the edge, especially when you need fast and frequent charging.
Tip: If you want to spend less time waiting for your battery to charge, sodium-ion technology offers a strong advantage.
Cycle Life
Cycle life tells you how many times a battery can charge and discharge before it loses much of its power. You want a battery that lasts a long time, especially if you use it every day. Let’s look at how sodium-ion and lithium-ion batteries perform over time.
Longevity of Sodium-ion
Sodium-ion batteries have made progress, but they still show shorter cycle life than lithium-ion batteries. You can expect most sodium-ion batteries to last between 1,000 and 4,000 cycles before their capacity drops a lot. This means you can charge and use them many times, but they may not last as long as some other options.
Several factors affect how long sodium-ion batteries last:
Factor | Impact on Longevity |
|---|---|
Design and materials of separators | Increased safety margins and extended battery lifespan |
Thermal stability | Better thermal management, reducing maintenance costs |
Chemical stability | Enhanced durability in harsh environments |
Charge-discharge cycle resilience | Longer system lifespans and operational reliability |
You will notice that sodium-ion batteries work well in places where safety and cost matter more than long-term durability. They handle heat better and use materials that resist damage. If you use them for energy storage or backup power, you may find their cycle life meets your needs.
Tip: Sodium-ion batteries are still developing. Future designs may last even longer.
Lithium-ion Durability
Lithium-ion batteries stand out for their long cycle life. You can find lithium-ion batteries, especially LiFePO₄ types, that last from 3,000 to over 5,000 cycles in real-world use. This means you get more years of service before you need a replacement.
Lithium-ion batteries usually last longer than sodium-ion batteries.
Quality LiFePO₄ cells can exceed 5,000 cycles.
Sodium-ion batteries often show more wear after 1,000 to 4,000 cycles.
You will see lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles, laptops, and phones because they keep working well after many charges. Their durability makes them a top choice for devices you use every day.
Note: If you want a battery that lasts the longest, lithium-ion is still the leader.
Safety
Stability and Risks
When you choose a battery, safety should be one of your top concerns. Both sodium-ion and lithium-ion batteries have unique safety profiles. You will see some important differences in the table below:
Battery Type | Safety Risk Description |
|---|---|
Lithium-Ion | Medium risk of thermal runaway; can be flammable or explode if damaged or in extreme conditions. Needs charge for storage. |
Sodium-Ion | Safer, lower risk of thermal runaway; non-flammable. Can be safely discharged to 0V. |
Lithium-ion batteries can catch fire or even explode if they get too hot or suffer damage. You must store them with some charge, which adds another risk. Sodium-ion batteries do not burn easily. You can safely discharge them all the way to zero volts, which makes them safer to store and transport.
Let’s look at more details:
Feature | Sodium-Ion Batteries | Lithium-Ion Batteries |
|---|---|---|
Risk of Thermal Runaway | Lower risk | Medium risk |
Flammability | Non-flammable | Can be flammable |
Safe Discharge | Yes, to 0V | No |
Temperature Sensitivity | Wide range | Sensitive |
Note: Sodium-ion batteries work in a wider range of temperatures. You do not have to worry as much about overheating or cold weather.
Application Safety
You will find that both battery types use special safety features in electric vehicles and energy storage systems. Sodium-ion batteries have better thermal stability, which lowers the risk of fire. This makes them a good choice for large battery banks or backup power. However, sodium-ion batteries can still face thermal runaway in rare cases, so you should always follow safety guidelines.
Lithium-ion batteries use many built-in safety mechanisms, like thermal cut-offs and pressure valves. These features help reduce the risk of fire or explosion, but lithium-ion batteries still have moderate safety concerns. You must handle them with care, especially in high-power uses like electric cars.
Sodium-ion batteries: safer, less likely to catch fire, can be stored at zero charge.
Lithium-ion batteries: more safety features, but higher risk if damaged or overheated.
If you want a battery with fewer safety worries, sodium-ion batteries offer peace of mind for most uses.
Cost and Supply Chain
Material Costs
You might think sodium-ion batteries cost less because sodium is easy to find. In reality, prices for sodium-ion batteries in China are much higher than for lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries. The cost difference comes from the new technology and the need for more research and development. Lithium prices have dropped, making LFP batteries even more affordable. This change reduces the price advantage for sodium-ion batteries.
Here is a quick look at material costs:
Battery Type | Material Cost Insights |
|---|---|
Sodium-ion | Prices in China are significantly influenced by commercialization activities, with costs potentially twice that of LFP batteries. |
Lithium-ion (LFP) | The price forecast for LFP material is provided, indicating its relevance in comparison to sodium-ion technology. |
You should know that mixed metal oxide cathode materials are important for reaching the energy density needed in cars and trucks. Right now, sodium-ion batteries use materials that cost more to produce at scale.
Sodium-ion batteries are currently priced significantly higher than LFP batteries in China.
The decline in lithium prices has reduced the competitive edge of sodium-ion batteries.
Mixed metal oxide cathode materials are crucial for achieving necessary energy density in automotive applications.
Tip: If you want the lowest battery cost today, LFP lithium-ion batteries are the better choice.
Market Readiness
You see sodium-ion batteries gaining attention because they promise lower costs and better safety. However, most sodium-ion batteries are still in the early stages of development. They face challenges like lower energy density and a lack of strong market infrastructure. Companies in China are investing in sodium-ion technology, but these batteries are not ready for large-scale use yet.
Let’s compare supply chain stability:
Aspect | Sodium-Ion Batteries | Lithium-Ion Batteries |
|---|---|---|
Availability | Abundant and globally available | Concentrated in specific geographic areas |
Price Volatility | Less prone to price fluctuations | Characterized by rising costs and volatility |
Supply Chain Security | More stable and secure | Faces significant supply risks |
You benefit from sodium’s global abundance and stable prices. Lithium supply chains can be risky and face price swings. Still, lithium-ion batteries have a strong market presence and support. Sodium-ion batteries need more time and investment before you see them everywhere.
Note: If you want a battery with proven market support and easy access, lithium-ion is the safer bet for now.
Environmental Impact
Sustainability
You want to know how batteries affect the planet. Sodium-ion and lithium-ion batteries have different impacts on the environment. Sodium is easy to find and spread across the world. Lithium is rare and found in only a few places. This makes sodium-ion batteries more sustainable when you look at raw materials.
Here is a table that shows how these batteries compare:
Category | Sodium-Ion Batteries | Lithium-Ion Batteries |
|---|---|---|
Greenhouse Gas Emissions | Lower per unit of energy produced | |
Resource Availability | Abundant and widely distributed | Scarce and concentrated |
Safety | Lower risk, non-flammable | Medium risk, flammable |
Recyclability | Complex, energy-intensive |
Sodium-ion batteries use sodium and aluminum, which cost less and are easier to get. Lithium-ion batteries need lithium, copper, cobalt, and nickel. These metals are expensive and hard to find. You see that sodium-ion batteries are safer because they do not catch fire easily. They also work better in extreme temperatures.
Tip: If you care about using earth-friendly materials, sodium-ion batteries offer a better choice for sustainability.
Recycling
You might wonder what happens to batteries when they reach the end of their life. Most lithium-ion batteries end up in landfills. Only about 5% get recycled worldwide. Recycling lithium-ion batteries is hard and costs a lot. The process uses much energy and creates hazardous waste.
Sodium-ion batteries are easier to recycle. They do not contain toxic metals like cobalt or nickel. The recycling process is less dangerous and uses less energy. You can recycle sodium-ion batteries without creating harmful waste.
Sodium-ion batteries have a higher potential for non-toxic recycling.
Lithium-ion batteries often end up as hazardous waste.
Recycling sodium-ion batteries is safer and simpler.
If you want a battery that is easier to recycle and safer for the environment, sodium-ion batteries stand out. You help reduce pollution and protect nature by choosing batteries with better recycling options.
Applications

Electric Vehicles
You see electric vehicles everywhere now. Lithium-ion batteries power most electric cars, bikes, and scooters. These batteries give you high energy density and light weight, which means your car can travel farther before you need to recharge. You find lithium-ion batteries in popular brands like Tesla and Nissan. They help you drive longer distances and enjoy quick acceleration.
Sodium-ion batteries are starting to appear in electric mobility. Some companies use them in buses and delivery vehicles. These batteries offer fast charging and lower costs. You may not get the same range as lithium-ion, but sodium-ion batteries work well for short trips and city driving.
Battery Type | Common Applications |
|---|---|
Sodium-Ion | Electric mobility (buses, delivery vehicles), Grid-scale energy storage |
Lithium-Ion | Electric cars, bikes, scooters, Portable electronics |
Tip: If you want a car with long range, lithium-ion batteries are the best choice. For city transport or short routes, sodium-ion batteries can save you money.
Energy Storage
You need reliable energy storage for your home or business. Sodium-ion batteries shine in grid-scale energy storage and renewable energy systems. You see them in solar farms and wind power stations. These batteries store extra energy and release it when demand is high. They also work well for backup power in factories and offices.
Lithium-ion batteries also play a big role in energy storage. You find them in home battery systems and commercial backup units. They offer high energy density, so you can store more power in less space.
Sodium-ion batteries: Grid storage, renewable energy, industrial backup
Lithium-ion batteries: Home energy storage, commercial backup, portable power banks
Note: Sodium-ion batteries are a smart pick for large-scale storage. Lithium-ion batteries fit best in smaller systems.
Consumer Devices
You use lithium-ion batteries every day. They power your phone, laptop, tablet, camera, and power tools. These batteries keep your devices light and slim. You can carry them easily and use them for hours without charging.
Sodium-ion batteries are less common in consumer electronics. You may see them in some commercial energy storage products. Their larger size and lower energy density make them less suitable for small gadgets.
Lithium-ion batteries: Phones, laptops, tablets, cameras, power tools
Sodium-ion batteries: Commercial energy storage, backup power systems
If you want long-lasting, lightweight devices, lithium-ion batteries are your best option.
Future Outlook
Technology Development
You will see exciting changes in battery technology over the next few years. Sodium-ion batteries are gaining attention for specific uses, especially in low-voltage systems and large energy storage projects. Companies are working to improve the design and materials of sodium-ion batteries. These efforts focus on making them safer, cheaper, and easier to recycle. You may notice that sodium-ion batteries have about 30% less energy density than lithium-ion batteries. This makes them less suitable for electric vehicles that need to travel long distances. However, researchers continue to look for ways to boost their performance. You might see new breakthroughs in electrode materials or manufacturing methods. These changes could help sodium-ion batteries close the gap with lithium-ion batteries in the future.
Scientists expect sodium-ion battery production capacity to reach 6.4 terawatt hours by 2030. This number shows strong growth, but it still falls short of the projected demand of 7.6 terawatt hours.
Adoption Trends
You will notice different adoption rates for sodium-ion and lithium-ion batteries. Lithium-ion batteries remain the top choice for electric vehicles because they offer higher energy density and have well-established supply chains. Most car makers use lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries, which are affordable and reliable. Sodium-ion batteries are starting to gain market share, especially in energy storage. Experts predict that sodium-ion batteries will grow from 5% to 30% of the market by 2030. By 2026, about 70% of sodium-ion batteries will be used for energy storage, while only 18% will go into electric vehicles. You may see more sodium-ion batteries in solar farms, wind power stations, and backup systems. These trends show that sodium-ion batteries will play a bigger role in supporting renewable energy and grid stability.
🔋 Sodium-ion batteries: Rapid growth in energy storage, limited use in electric vehicles.
🚗 Lithium-ion batteries: Dominant in electric vehicles, steady presence in consumer devices.
You can expect sodium-ion batteries to become more common in large-scale energy projects. Lithium-ion batteries will continue to lead in cars and portable electronics.
You see that lithium-ion batteries give you higher energy density and longer life for electric vehicles and devices. Sodium-ion batteries offer faster charging and safer storage for large energy projects. Check the table below for a quick guide:
Best For | Lithium-Ion | Sodium-Ion |
|---|---|---|
Electric Vehicles | ✅ | |
Energy Storage | ✅ | |
Consumer Devices | ✅ |
Tip: Think about your needs. If you want top performance in cars or gadgets, choose lithium-ion. For safe, affordable energy storage, sodium-ion works best. Watch for new battery technology in the future.
FAQ
What makes sodium-ion batteries safer than lithium-ion batteries?
You get safer storage with sodium-ion batteries. They do not catch fire easily. You can discharge them to zero volts. Lithium-ion batteries need careful handling because they can overheat or explode.
Can you use sodium-ion batteries in smartphones or laptops?
You will not see sodium-ion batteries in most phones or laptops. Their lower energy density makes them too heavy and bulky for small devices. Lithium-ion batteries work better for portable electronics.
Are sodium-ion batteries better for the environment?
You help the planet by choosing sodium-ion batteries. They use common materials and avoid rare metals. Recycling is easier and less toxic. Lithium-ion batteries create more hazardous waste.
How long does it take to charge a sodium-ion battery?
You can charge a sodium-ion battery in about 20 minutes. Some designs reach 80% in just 6 minutes. Lithium-ion batteries usually take longer to charge.
Quick Link
Contact
Address
Floor 18, Yuehu Jinhui Tower, 225 Liuting Street Haishu District,Ningbo,China 315010
Copyright © 2025 , All rights reserved. Powered by ningbo v.k. industry & trading Co., Ltd.